Who Started Education in India is a question that opens the door to a rich and fascinating history spanning thousands of years.
Ancient India’s educational heritage has had a profound impact on the country’s cultural and intellectual development.
The significance of understanding who initiated education in this region cannot be overstated, as it has shaped the course of Indian history.
By exploring the roots of Indian education, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s academic traditions.
The Ancient Roots of Indian Education
The roots of education in India stretch back thousands of years, nourished by the Vedic education system and the Gurukul tradition. This ancient heritage has significantly influenced the country’s educational landscape.
The Vedic Education System
The Vedic education system was a sophisticated and comprehensive method of learning that focused on the Vedas, ancient Indian texts considered sacred. It was characterized by a strong emphasis on spiritual growth, philosophical inquiry, and the development of character.
Role of Rishis and Scholars
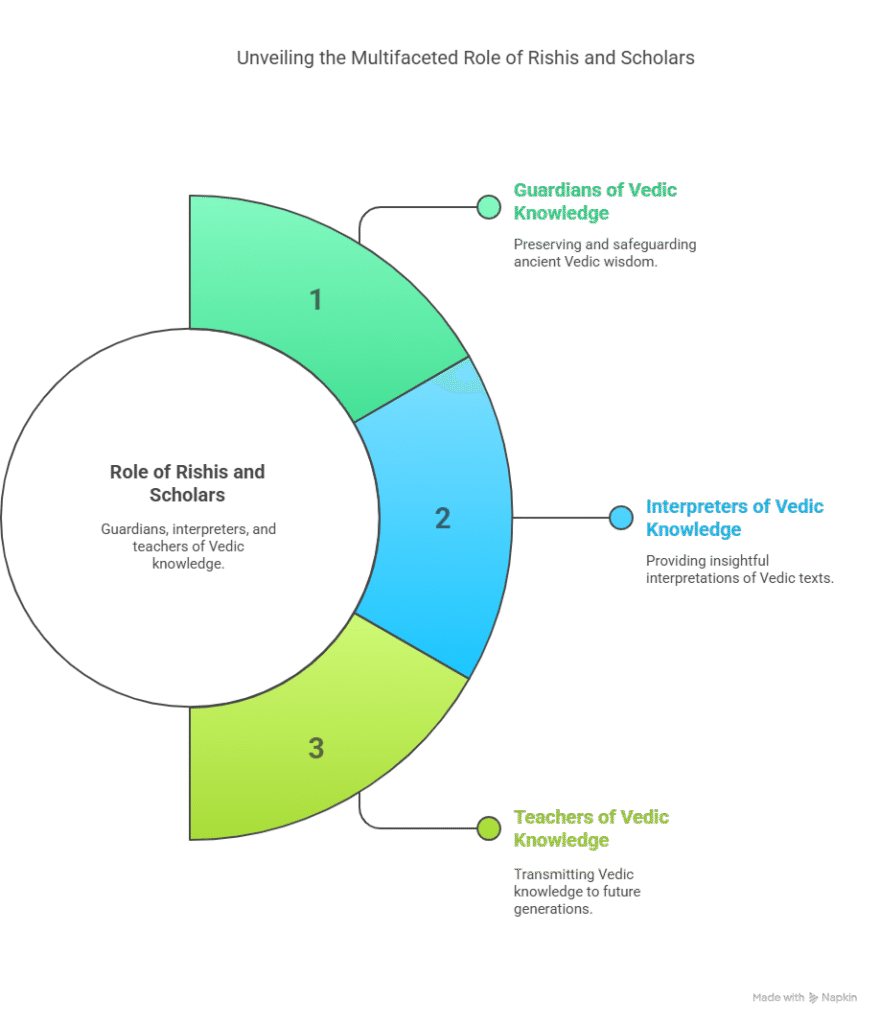
Rishis and scholars played a pivotal role in the Vedic education system. They were not only the guardians of the Vedic knowledge but also its interpreters and teachers. Their role was crucial in preserving and transmitting the ancient wisdom to successive generations.
Teaching Methods and Curriculum
The teaching methods in the Vedic education system were diverse, including discussion, debate, and reflection. The curriculum was broad, encompassing not just religious texts but also subjects like mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. This holistic approach aimed at developing well-rounded individuals.
| Subject | Description |
|---|---|
| Vedic Studies | Study of the Vedas and related texts |
| Philosophy | Exploration of metaphysical and ethical questions |
| Science and Mathematics | Study of astronomy, mathematics, and other sciences |
Gurukul Tradition and Its Significance
The Gurukul tradition was an integral part of ancient Indian education, where students lived with their teachers (Gurus) and learned not just academic subjects but also life skills and values. This system fostered a close bond between the teacher and the student, facilitating a comprehensive education.
Structure of Gurukuls
Gurukuls were typically residential schools where students from various backgrounds came to live and study together. The structure was informal, with learning happening through discussions, practical work, and community living.
Famous Ancient Learning Centers
Ancient India was home to several renowned learning centers, such as Nalanda University and Takshashila University, which attracted scholars from across the world. These institutions were hubs of intellectual inquiry and innovation.
Who Started Education in India: Key Historical Figures
Understanding who started education in India requires a look into the lives and contributions of its ancient scholars. The history of Indian education is a rich and diverse tapestry, influenced by various philosophical, religious, and cultural traditions.
Ancient Scholars and Their Contributions
Ancient India was home to a plethora of scholars who significantly contributed to the development of education. Their contributions span various fields, including philosophy, literature, and science.
Vedic Sages and Their Educational Philosophy
The Vedic sages played a pivotal role in shaping the educational philosophy of ancient India. They emphasized the importance of knowledge (jnana) and spiritual growth, laying the foundation for a holistic approach to education.
Contributions of Panini, Chanakya, and Other Scholars
Scholars like Panini and Chanakya made significant contributions to various fields. Panini’s work on Sanskrit grammar is considered a landmark in linguistic studies, while Chanakya’s Arthashastra remains a seminal work on political economy and statecraft.
| Scholar | Contribution | Field |
|---|---|---|
| Panini | Sanskrit Grammar | Linguistics |
| Chanakya | Arthashastra | Political Economy |
| Vedic Sages | Vedic Knowledge | Philosophy & Spirituality |
Buddhist and Jain Influence on Indian Education
The Buddhist and Jain traditions also had a profound impact on Indian education. They promoted a culture of learning and intellectual inquiry, establishing institutions that became centers of academic excellence.
Nalanda, Takshashila, and Other Universities
Institutions like Nalanda and Takshashila were renowned for their academic excellence. Nalanda, in particular, was a major center for Buddhist learning, attracting scholars from across Asia.
Educational Reforms During Medieval Period
During the medieval period, educational reforms continued, with various rulers and scholars contributing to the evolution of the Indian education system.

Conclusion: The Legacy of Indian Education
Understanding who started education in India and the rich history of education in India is crucial to appreciating the country’s educational heritage. The ancient roots of Indian education, shaped by the Vedic education system and the Gurukul tradition, have had a lasting impact on the country’s learning landscape.
The contributions of ancient scholars, as well as Buddhist and Jain influences, have also played a significant role in shaping Indian education. By exploring the history of education in India, we can gain a deeper understanding of the values and principles that have guided the country’s educational institutions for centuries.
As we reflect on the legacy of Indian education, we are reminded of the importance of preserving and promoting this rich heritage for future generations. By doing so, we can continue to draw inspiration from the past and build a stronger foundation for education in India.
FAQ
Who is credited with starting education in India?
The origin of education in India dates back to the Vedic period, with the Vedic sages and Rishis playing a significant role in shaping the country’s educational landscape.
What is the history of education in India?
The history of education in India is rich and diverse, with roots in ancient traditions such as the Vedic education system and the Gurukul system. These systems emphasized the development of the individual and society through various subjects, including philosophy, literature, and science.
What were the key features of ancient education in India?
Ancient education in India was characterized by a strong emphasis on spiritual and philosophical knowledge, as well as a holistic approach to learning. The Gurukul tradition, for example, focused on the all-round development of students, including their physical, mental, and spiritual well-being.
What were some of the most famous educational institutions in ancient India?
Some of the most renowned educational institutions in ancient India include Nalanda University, Takshashila University, and the Gurukuls established by various Rishis and scholars. These institutions attracted students from across the country and abroad, contributing to the exchange of knowledge and ideas.
How did Buddhist and Jain traditions influence Indian education?
Buddhist and Jain traditions had a significant impact on Indian education, with institutions like Nalanda and Takshashila becoming centers of learning for Buddhist and Jain scholars. These traditions introduced new perspectives and approaches to education, enriching the overall educational landscape.
What is the significance of understanding the history of education in India?
Understanding the history of education in India provides valuable insights into the country’s cultural and intellectual heritage. It highlights the contributions of ancient scholars and institutions, as well as the evolution of educational thought and practices over time.
Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=izTVekJ__yA
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z2pD5F8piYw




